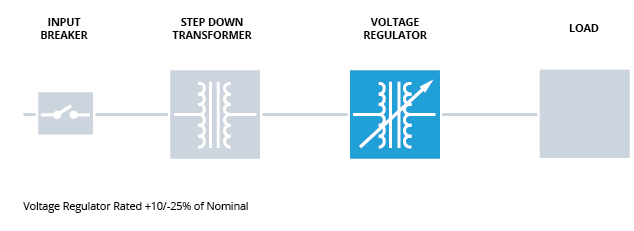
FIGURE 2: System with variable input voltage corrected by using a voltage regulator.
Figure 2 depicts a base system with an automatic voltage regulator on the low-voltage side of the step-down transformer. For analysis, at an instant of time, the voltage regulator simply acts as a transformer with a fixed turns ratio. The turns ratio is determined by the system’s need to buck or boost the output voltage of the step-down transformer, based upon voltage delivered by the source to the step-down transformer input.
For example, if the system delivers voltage that is 15% below the nominal or desired system voltage, the regulator is responsible for boosting the voltage by 17.65% (1.0/0.85). As such, the regulator acts as a transformer with a turns ratio of 1 to 1.1765. Now, this instant-of-time analysis can be performed simply by noting the transformation ratio of the two transformers – specifically the required range of current and voltage for each system component as a function of the input system voltage and the load it serves.

